Lotus reveals new insight into its electric sports car platform
Innovative and flexible platform to underpin Lotus’s 2026 EV sports car
Lotus has released new details about its innovative lightweight electric vehicle architecture (LEVA) that will go on to underpin both its own all-electric sports car due in 2026, and be licenced to clients through its Lotus Engineering sub-brand.
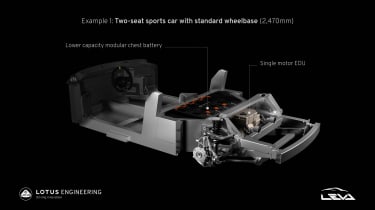
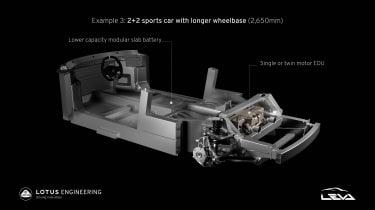
What’s been revealed is the extent to which this new architecture, which is constructed from the same bonded aluminium method as it pioneered with the original Elise, can be varied depending on its application. This variation is obviously key to its flexibility, but doesn’t just come with variations in size and proportion, but also layout, with an industry-first application of variable battery placements within a single chassis design.
Models built on this architecture with two seats will utilise a ‘chest’ battery layout, which places the batteries in a vertical casing behind the rear seats. There are two battery capacities available for this layout, 66.4kWh and 99.6kWh, that then determine the minimum and maximum lengths of the respective models. Each battery pack will then support either single or dual motor layouts specific to the two battery capacities, producing total power figures of 350kW (469bhp) or 650kW (871bhp).
Two-plus-two models, like the original Evora, will swap this layout for a more common ‘slab’ battery layout, which will sit horizontally under the cabin floor, albeit in just the smaller 66.4kWh capacity. This chassis option will then be available with both single and dual motor options.
Both layouts have their inherent pros and cons thanks to where the mass sits within the chassis, but whereas you might think models fitted with a stacked battery pack might be at a disadvantage thanks to a higher centre of gravity, many engineers continue to struggle with developing ride and handling packages that deal with the physics associated with a driver being sat directly above, not in the midst of so much weight. The stacked batteries will also allow lotus engineers to mount the seat much lower than in a car, again mimicking the weight distribution of traditional IC cars.
Despite this vastly different powertrain layout, many elements of this electric architecture have been derived from the Emira sports car, with the biggest differentiator being the rear subframe. With the need to only support a compact electric motor and not a V6 engine and transmission, it’s 37 percent lighter than the one used in the Emira.
So Lotus has started revealing its cards, and while EVs currently seem focused on big saloons and SUVs, it’s looking like the wait won’t be long until more evo-centric electric models eventually arrive. Like Lotus did with the Elan and Elise, it’s once again acting as a visionary of the sports car genre, and on this initial tech drop they might well be onto something.